Drugs of Abuse Frequently Asked Questions
- Marijuana
- Cocaine
- Opiates
- Heroin
- Amphetamines
- Methamphetamines
- MDMA or Ecstasy
- PCP or Angel Dust
- Barbiturates
- Antidepressants
- Methadone
Marijuana drug testing facts:
What is Marijuana?
Marijuana is a green or gray mixture of dried, shredded flowers and leaves of the hemp plant Cannabis sativa.
|

|

|
|

Hemp Plant Cannabis Sativa
|

Cannabis In a Dried Form
|
How is Marijuana consumed?
It is usually smoked as a cigarette (called a joint or a nail) or in a pipe or bong. In recent years, it has appeared in blunts. These are cigars that have been emptied of tobacco and re-filled with marijuana, often in combination with another drug, such as crack. Some users also mix marijuana into foods or use it to brew tea.
What are the effects of Marijuana?
The short-term effects of marijuana use include problems with memory and learning; distorted perception; difficulty in thinking and problem solving; loss of coordination; and increased heart rate, anxiety, and panic attacks. Marijuana users experience the same health problems as tobacco smokers, such as bronchitis, emphysema and bronchial asthma. Some of the effects of marijuana use also include: an increased heart rate, dryness of the mouth, reddening if the eyes, impaired motor skills and concentration, and frequent hunger and an increased desire for sweets. Occasionally hallucinations, fantasies and paranoia are reported.
How can you tell if someone has been using marijuana?
If someone is high on marijuana, he or she might
* seem dizzy and have trouble walking;
* seem silly and giggly for no reason;
* have very red, bloodshot eyes; and
* have a hard time remembering things that just happened.
When the early effects fade, over a few hours, the user can become very sleepy.
What are common street names for Marijuana?
There are over 200 slang terms for marijuana including "pot," "herb," "weed," "boom," "Mary Jane," "gangster," and "chronic."
What is the detection period for Marijuana?
Marijuana is detectable in urine for 48-72 hours after single use. Habitual or chronic use can be detected in urine for up to 12 weeks depending on quantity, duration, and frequency of use. It is advised to establish a random marijuana drug testing at home at a very early age.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Substances that may cause a false positive are:
Efavirenz (Sustiva)
Dronabinol (Marinol) (True Positive)
Hempseed Oil (True Positive)
Back to top
Cocaine:
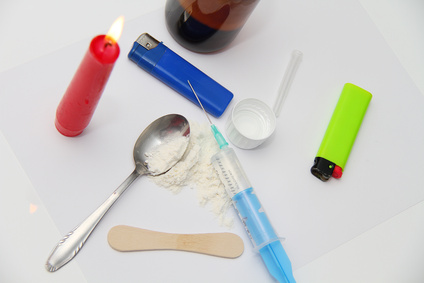
What is Cocaine?
In its pure form, cocaine is a white crystalline powder extracted from the leaves of the South American coca plant. On the street, pure cocaine is diluted or "cut" with other substances to increase the quantity, and thereby increase the profits of its sellers.
|
|

|
|

Various Forms of Cocaine
|

Coca Plant
|
How is Cocaine consumed?
Cocaine users most often inhale the powder sharply through the nose, where it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream. But it also can be heated into a liquid and its fumes inhaled through a pipe in a method called "freebasing". Freebasing is also a common method of using a form of cocaine called "crack". Crack resembles small pieces of rock and is often called "rock" on the street.
What are the effects of Cocaine?
Addicts are preoccupied with getting their drug, and most of their thoughts and behaviors are directed to that end. Cocaine interferes with judgment and produces exaggerated feelings of well-being and confidence. High doses can produce paranoia, and users can become aggressive and violent. In rare cases, cocaine can produce death, after first use or after prolonged use. Death occurs from cardiac arrest (the person's heart stops beating), or seizures followed by respiratory arrest (the person stops breathing). Some signs of use may include: dilation of the pupils, runny or stuffed-up nose, inflammation of the nasal membranes, less need for food or rest, more talkative and sociable.
What are common street names for Cocaine?
Some common street names for cocaine are: Coke, blow, powder, sugar, nose candy, rock, crack, and base.
What is the detection period for Cocaine?
Cocaine is detectable in urine for 48-72 hours after use. Very low concentrations of cocaine may be detected in urine during the initial several hours, but benzoylegonine persists in urine at detectable concentrations for 48 hours. Long-term habitual users may have traces of cocaine remain in their system for longer than the standard 3 days.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Substances that may cause a false positive are:
Isoxsuprine (Vasodilan)
Some Inca Teas (True Positive
Back to top
Opiates:
What are opiates?
Opiates are narcotics that contain Opium. Opium is derived from the pod of the poppy Papover somniferum. There are two processes that remove the extract. The narcotics which opium is an ingredient in are: Morphine, Codeine, Thebaine and Heroin (see Heroin section). Morphine is used exclusively in hospitals, excluding the use by drug abusers, as a pain reliever. Codeine is produced from morphine and is found in several legal products outside of a hospital. It is for moderate pain relief and is sometimes combined with aspirin, acetaminophen, Robitussin AC, Cheracol and elixir of terpin hydrate. Thebaine is a minor constituent of opium, an alkaloid present in another species of poppy Papover bracteatum. Although thebaine is like morphine and codeine, it produces stimulant effects rather than a depressant effect.
|

|

|
|

Opium Poppy Flower
|

Poppies
|
How are opiates consumed?
It is allowed into the body in several ways including: injection under the skin, intramuscularly, or intravenously. It is also marketed as white crystals for smoking, and tablets for oral ingestion. Most of the morphine obtained from opium is converted to codeine, and secondarily, to hydro morphine.
What are the effects of Opiates?
General effects of narcotic analgesics include: sedation, slowed reflexes, raspy speech, sluggish "rubber-like" movements, slowed breathing, cold skin, and possible vomiting. However, as a user continues to abuse narcotic analgesics he or she will build a tolerance to the drug, therefore causing the effects to diminish. If the abuser wishes to maintain the same effect, he or she will have to take steadily larger doses as the tolerance develops. If a user is addicted to opiates he or she will suffer withdrawal symptoms if they don't receive another dose, or "fix", before the drug is completely out of their system. Withdrawal effects can be chills, aches of the muscles and joints, nausea and insomnia.
What are common street names for Opiates?
Some common street names for opiates include:
Morphine: M, Miss Emma, Mister Blue, and Morph
Codeine: Schoolboy
Dilaudid: Lords
Methadone: Fizzies, Dollies
What is the detection period for Opiates?
Opiates can stay in your system for anywhere between 1-4 days. Morphine stays in the body for at least 84 hours; Codeine, for at least 2-5 days; and Opium for 24-48 hours.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Substances that may cause a false positive are:
Poppy Seeds (True Positive)
Tylenol with codeine (True Positive)
Most prescription pain medications
Back to top
Heroin:
What is Heroin?
Heroin is an illegal, highly addictive drug. It is both the most abused and the most rapidly acting of the opiates. It is typically sold as a white or brownish powder or as the black sticky substance known on the streets as "black tar heroin." Although purer heroin is becoming more common, most street heroin is "cut" with other drugs or with substances such as sugar, starch, powdered milk, or quinine. Street heroin can also be cut with strychnine or other poisons. Because heroin abusers do not know the actual strength of the drug or its true contents, they are at risk of overdose or death.
|

|

|
|

Samples of Heroin
|

Heroin (powdered form)
|
How is Heroin consumed?
Heroin is usually injected, sniffed/snorted, or smoked. Although smoking and sniffing heroin do not produce a "rush" as quickly or as intensely as intravenous injection, NIDA researchers have confirmed that all three forms of heroin administration are addictive.
What are the effects of Heroin?
One of the most detrimental long-term effects of heroin is addiction itself. Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disease, characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, and by neurochemical and molecular changes in the brain. Heroin also produces profound degrees of tolerance and physical dependence, which are also powerful motivating factors for compulsive use and abuse. As with abusers of any addictive drug, heroin abusers gradually spend more and more time and energy obtaining and using the drug. Once they are addicted, the heroin abusers' primary purpose in life becomes seeking and using drugs. The drugs literally change their brains. Opiates tend to relax the user. When opiates are injected, the user feels an immediate "rush." Other initial and unpleasant effects include restlessness, nausea, and vomiting. The user may go "on the nod," going back and forth from feeling alert to drowsy. With very large doses, the user cannot be awakened, pupils become smaller, and the skin becomes cold, moist, and bluish in color. Breathing slows down and death may occur.
What are common street names for Heroin?
Street names associated with heroin include "smack," "H," "skag," and "junk." Other names may refer to types of heroin produced in a specific geographical area, such as "Mexican black tar."
What is the detection period for Heroin?
Heroin can stay in your system for up to 4 days after initial use. Long-term habitual users may have traces of heroin remain in their system for longer than the standard detection period.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Substances that may cause a false positive are:
Poppy Seeds
Tylenol with codeine
Most prescription pain medications
Back to top
Amphetamines:
What are amphetamines?
The amphetamines are potent psychomotor stimulants. Their use causes a release of the excitatory neurotransmitters dopamine and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) from storage vesicles in the Central Nervous System. Amphetamines are a whole family of related drugs - each with its own recipe - and are taken in different ways. They can be in the form of powder, tablets, capsules, crystals or red liquid. They can come as a white through to a brown powder, sometimes even orange and dark purple. Amphetamines have a strong smell and bitter taste.
|

|

|
|

Amphetamine Capsules
|

Amphetamine Crystals
|
How are amphetamines consumed?
Amphetamines may be sniffed, swallowed, snorted or injected.
What are the effects of amphetamines?
Amphetamines speed up the body's activity. Heart rate, breathing and blood pressure increase. A dry mouth, increased sweating, enlargement of the eye's pupils and headaches may occur. Users can feel energetic and full of confidence, with a heightened sense of well-being. Other effects include feeling wide-awake and alert, becoming talkative, restless, excited, and having difficulty sleeping. Panic attacks may also be experienced. Withdrawal symptoms may include hunger, extreme fatigue, anxiety, irritability, and depression. People may also have a long but restless sleep, often interrupted by nightmares. Some experience severe distress or feelings of panic.
What are common street names for amphetamines?
The common names are speed, up, fast, louee, goey, whiz, pep pills, and uppers.
What is the detection period for amphetamines?
Amphetamines are normally detectable in urine for 24-72 hours after use.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Some substances that may cause false positives include:
Amphetaminil
Adderall (True Positive)
Clobenzorex (Asenlix)
Deprenil (Selegiline Eldepryl)
Benzphetamine (Didrex)
Dimethylamphetamine
Ethylamphetamine
Famprofazone
Fencamine
Fenethylline
Fenproporex
Furfenorex
Mefenorex
Mesocarb
Prenylamine
Phentermine
Back to top
Methamphetamine:
What is Methamphetamine?
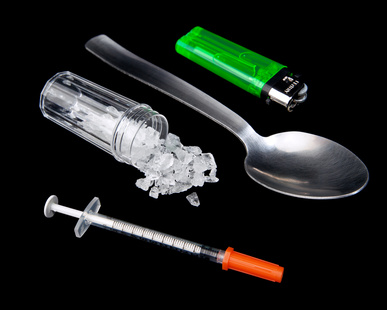
Methamphetamine is a powerfully addictive stimulant that dramatically affects the central nervous system. The drug is made easily in clandestine laboratories with relatively inexpensive over-the-counter ingredients. These factors combine to make methamphetamine a drug with high potential for widespread abuse. It is a white, odorless, bitter-tasting crystalline powder that easily dissolves in water or alcohol.
|
|

|
|

Methamphetamine Crystals
|

TPowerfully Addictive
|
How is Methamphetamine consumed?
Meth can be smoked, snorted, injected, or taken orally, and its appearance varies depending on how it is used.
What are the effects of methamphetamine?
Like amphetamine, it causes increased activity, decreased appetite, and a general sense of well-being. The effects of methamphetamine can last 6 to 8 hours. After the initial "rush," there is typically a state of high agitation that in some individuals can lead to violent behavior. As a powerful stimulant, methamphetamine, even in small doses, can increase wakefulness and physical activity and decrease appetite. Those who smoke or inject methamphetamine report a brief, intense sensation, or rush. Oral ingestion or snorting produces a long lasting high instead of a rush, which reportedly can continue for as long as half a day.
What are common street names for methamphetamine?
Methamphetamine is commonly known as "speed," "meth," and "chalk." In its smoked form it is often referred to as "ice," "crystal," "crank," and "glass."
What is the detection period for methamphetamine?
Amphetamines are normally detectable in urine for 24-72 hours after use. Methamphetamines stay in the system slightly longer, 24-96 hours.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Some substances that may cause false positives include:
Benzphetamine (Didrex)
Deprenyl (Eldepryl, Selegiline)
Dimethylamphetamine
Famprofazone
Fencamine
Furfenorex
Vick's Inhaler (Deoxyephedrine)
Ranitidine (Zantac)
High doses of Ephedrine/Ma Hunag
Back to top
MDMA or Ecstasy:
What is MDMA?
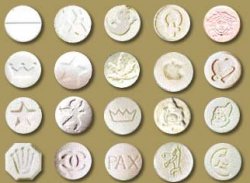
MDMA, or 'ecstasy' is a 'psychedelic amphetamine' that has gained popularity over the past 20 years because of its ability to produce strong feelings of comfort, empathy, and connection to others. It most frequently comes in tablet form, although it is occasionally sold in capsules or as powder. Because MDMA is so popular and because it goes well with dance parties, the demand for it usually exceeds supply--especially at any given location on any given night. This creates an opening for unscrupulous individuals to sell virtually anything as 'ecstasy'. While 'ecstasy' is the popular name for MDMA, the functional definition of ecstasy is any pill represented as MDMA on the street. Ecstasy pills are notoriously unreliable in content, more so than most other street drugs, and commonly can contain caffeine, ephedrine, amphetamines, and don't necessarily contain MDMA or any psychoactive.
|
|
|

Ecstasy (MDMA) Tablets
|
How is MDMA consumed?
It is most frequently used orally and rarely snorted.
What are the effects of MDMA?
Depending on how much and how recently one has eaten, MDMA generally takes 30-60 minutes (although sometimes as long as 2 hours) to take effect. Unlike with many other psycho actives, the onset of MDMA is very quick. Often at the point one realizes that perhaps they are starting to notice effects, they are already 'launching' quickly towards the peak. This quick and extremely sharp 'launch' can be unnerving, feeling a bit like it's too quick and hard to know when it's going to end, but the feeling generally only lasts a few minutes until the full effects are reached. The primary effects of MDMA last approximately 3-4 hours when taken orally. For many people there is an additional period of time (2-6 hrs) where it is difficult to go to sleep and there is definitely a noticeable difference from everyday reality, but which is not strong enough to be considered 'tripping'. When the full effects of MDMA manifest, barring an uncommon negative reaction, users are likely to find that suddenly everything is right with the world. The primary effects sought by those using MDMA recreationally are the emotional openness, euphoria, stimulation, reduction of critical and cynical thoughts, and decrease of inhibitions that can accompany its use.
What are common street names for MDMA?
MDMA is most commonly known as Ecstasy or "E".
What is the detection period for MDMA?
Though MDMA is not specifically tested for in the standard 'NIDA-5" drug tests, it is chemically closely enough related to amphetamines that recent MDMA users will test positive in both amphetamines (a common test) and methamphetamines (a somewhat newer and less common test). Because of this, the detection periods for MDMA are going to be very similar to those for amphetamines. Another important point is that many tablets of street ecstasy are not pure MDMA and frequently includes amphetamines. Amphetamines are normally detectable in urine for 24-72 hours after use. Methamphetamines stay in the system slightly longer, 24-96 hours.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Some substances that may cause false positives include:
MDA (Methylenedioxyamphetamine)
MDEA (Methylenedioxyethylamphetamine)
Back to top
PCP or Angel Dust:
|
|

|
|
|

PCP or Angel Dust
|
What is PCP?
Phencyclidine (PCP) is a synthetic chemical in the dissociate anesthetic class. It is perhaps best known by the media hype it received in the late 1970's portraying it as a extremely dangerous chemical causing madness, psychotic reactions, and super-human strength. It is found in a variety of forms including crystals/powder, tablets, and liquid. PCP is used in very small quantities with 5-10 mg considered an average dose.
How is PCP consumed?
Recently it seems to be available on the underground market most commonly as cannabis joints, regular cigarettes or cannabis leaf dipped in liquid PCP, and usually marketed as something else, seldom as 'PCP'.
What are the effects of PCP?
Using PCP can cause Numbness; Cramps; Loss of muscular coordination; Nausea; Involuntary movements of the eyeballs; Problems with speaking; Decreased sensitivity to touch, pain and position. Chronic use will cause difficulty with thought, memory problems, stuttering, depression, anxiety and brain damage.
What are common street names for PCP?
PCP is commonly known as Angel Dust, Peace pill, Dust, Sherman's, Crystal, Rocket fuel, DOA, and Supergrass.
What is the detection period for PCP?
PCP is cleared from the bloodstream with a relatively long half life of 7-11 hours. Because it is a lipid (fat) soluble drug, detection in the urine is possible up to 48 hours or longer post dose.
Are there substances or conditions that may cause a false positive?
Venlafaxine (Effexor).
Back to top
Barbiturates:
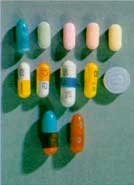
What are Barbiturates?
Barbiturates are basically the opposite of amphetamines: that is, they act to depress the central nervous system. In small doses they act as tranquilizers, but in larger doses they are sleeping pills. The sleep induced by barbiturates is not a normal sleep, in the sense that it seriously cuts down on the normal dream activity. Prolonged use of sleeping pills can lead to complete psychological crack-ups, as the mind has no way to release itself. Barbiturates are often a means of committing suicide.
|
|
|
|

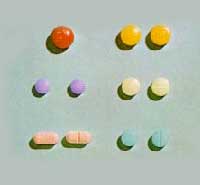
Barbiturate Samples
|

Barbiturate Tablets
|
How are Barbiturates consumed?
Barbiturates are taken orally or intravenously.
What are the effects of Barbiturates?
Barbiturates mimic alcohol inebriation. Mild euphoria, disinhibition, relief of anxiety, sleepiness can occur. In higher doses impairment of memory, judgment and coordination, irritability, paranoid and suicidal ideation can occur. The user may also experience sleepy, dizziness, nausea, slurred speech, and decreased respiration. Death occurs due to depression of the respiratory center in the brain. Tolerance develops quickly and larger doses are used, increasing the danger of an overdose.
What are common street names for Barbiturates?
Barbiturates are known as downers, barbs, red devils, goof balls, yellow jackets, block busters, pinks reds and blues, Christmas trees.
What is the detection period for Barbiturates?
Variable. Range of 3O hrs to several weeks depending on duration of action of the drug taken.
False Positive: Possibly Phenytoin (5.5 - Diphenylhydantoin)
Back to top
Antidepressants:
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) are commonly used for the treatment of depressive disorders. They have a half-life ranging from 2-70 hours. The are taken orally and sometimes by injection. TCAs are metabolized in the liver and excreted via the kidneys. TCA overdoses can result in the profound central nervous system depression, cardio toxicity and anticholineric effects. TCA overdose is the most common cause of death from prescription drugs.
TCA False Positive:
Quetiapine,
Carbamazepine (High dose),
Cyproheptadine ( Periactin)
Back to top
Methadone:
What is Methadone?
Methadone is a synthetic opioid. It is prescribed to dependent users of heroin and other opioids as a substitute for these drugs.
|
|
|

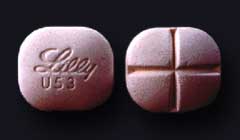
Methadone
|
How is methadone consumed?
In methadone maintenance treatment programs, methadone usually comes as a syrup that patients drink with fruit juice or cordial. Methadone is sometimes available in powder or tablet form. Methadone can be injected. Some users illicitly "divert" methadone from treatment programs and inject it, or sell it to others for this purpose.
What are the effects of Methadone?
Methadone has similar depressant and analgesic effects to other opioids. However, methadone's effects last much longer (24 hours as opposed to a few hours). Methadone does not have the euphoric effects that heroin does.
If an excessively low dose of methadone is prescribed, effects similar to those of heroin withdrawal may be experienced (that is, flu-like symptoms, nausea, diarrhea, aches, irritability and insomnia). On the contrary, an excessively high dose can cause similar effects to those associated with long-term heroin use (for example, drowsiness, nausea, dizziness, shallow breathing, low body temperature, slow pulse, heart palpitations).
Side effects of methadone (not related to the dosage level) can include excessive sweating, constipation, aches, rashes, fluid retention, loss of appetite and stomach cramps. Long-term methadone use causes tooth decay. Taking methadone in combination with other depressants increases the risk of overdose. If someone who is not dependent on opioids takes methadone the effects are very strong and the risk of overdose is very high.
What are common street names for Methadone?
Common street names are: done, junk, jungle juice, meth, and metho.
What is the detection period for Methadone?
Methadone can be detected in urine for up to 48 hours. Depending on duration of drug use, it may be detectable for up to a week.
Are there substances or conditions that my cause a false positive?
Like the other opioids, substances that may case false positives are:
Possible False Positive:
Due to metabolites of Disopyramide, Verapamil
Back to top |